In this post, I will walk you through how you can use AWS Lambda@Edge feature to redirect website visitors based on their browser language.
For instance, if a user arrives externally on the website homepage (English version) with an Italian browser he gets redirected to the Italian section of the website. To represent this use case, I created a static web site hosted on an S3 bucket, and a CloudFront distribution in top of the bucket:
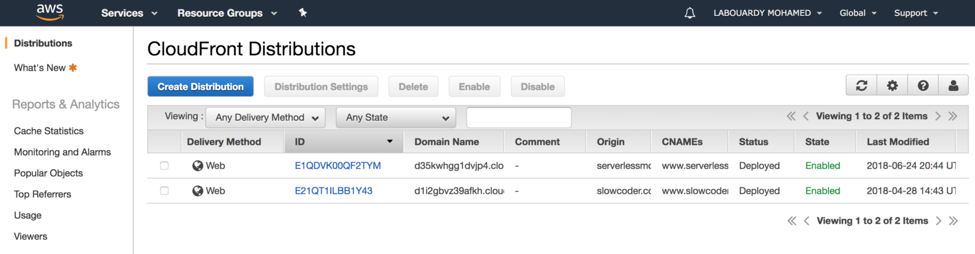
The following diagram illustrates how CloudFront distribution and Lambda@Edge will fit into the architecture:
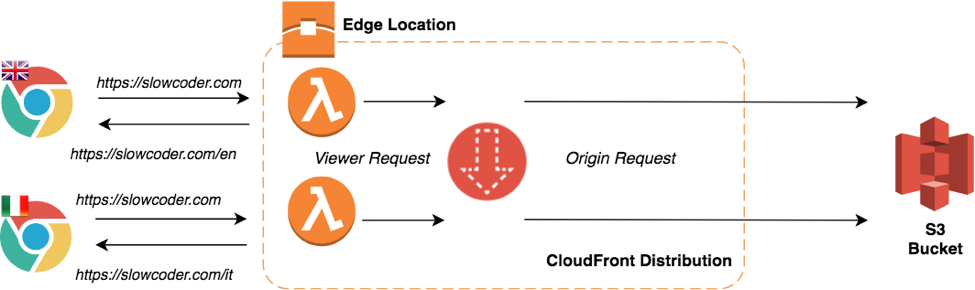
The AWS Lambda function will route the user’s request to relevant language of the website based on the request Accept-Language header property sent by the browser.
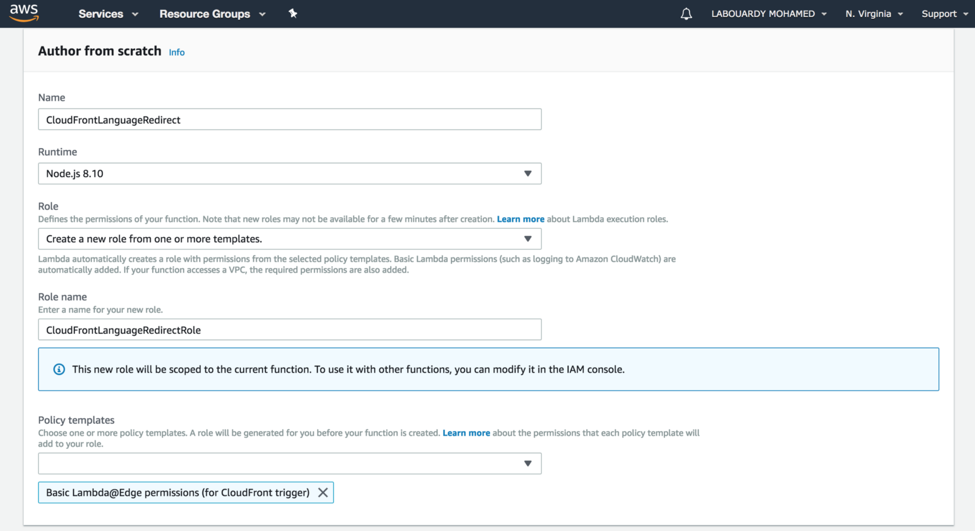
To get started, create a new Lambda function in the Virginia region (us-east-1). Attach an IAM role based on the Lambda@Edge policy template:
The code below is the function handler written in Node.JS. It should be quite readable and easy to port into other programming languages. It will identify the web browser language based on the Accept-Language header and redirect the homepage to the relevant language section of the website. Plus, it defines the english version to be the fallback URL if the Accept-Language isn’t actually defined.
exports.handler = (event, context, callback) => {
const request = event.Records[0].cf.request
const headers = request.headers
if(request.uri == '/') {
if (typeof headers['accept-language'] !== 'undefined') {
const supportedLanguages = headers['accept-language'][0].value
console.log('Supported languages:', supportedLanguages)
if(supportedLanguages.startsWith('en')){
callback(null, redirect('/en/'))
} else if(supportedLanguages.startsWith('fr')){
callback(null, redirect('/fr/'))
} else if(supportedLanguages.startsWith('it')){
callback(null, redirect('/it/'))
} else if(supportedLanguages.startsWith('pl')){
callback(null, redirect('/pl-PL/'))
} else {
callback(null, redirect('/en/'))
}
} else {
callback(null, redirect('/en/'))
}
} else {
callback(null, request)
}
};
function redirect (to) {
return {
status: '301',
statusDescription: 'redirect to browser language',
headers: {
location: [{ key: 'Location', value: to }]
}
}
}
In order to invoke the function above each time a client request is received by the CloudFront distribution, you need to attach the Lambda function to the Viewer Request trigger of your Amazon CloudFront distribution behavior:
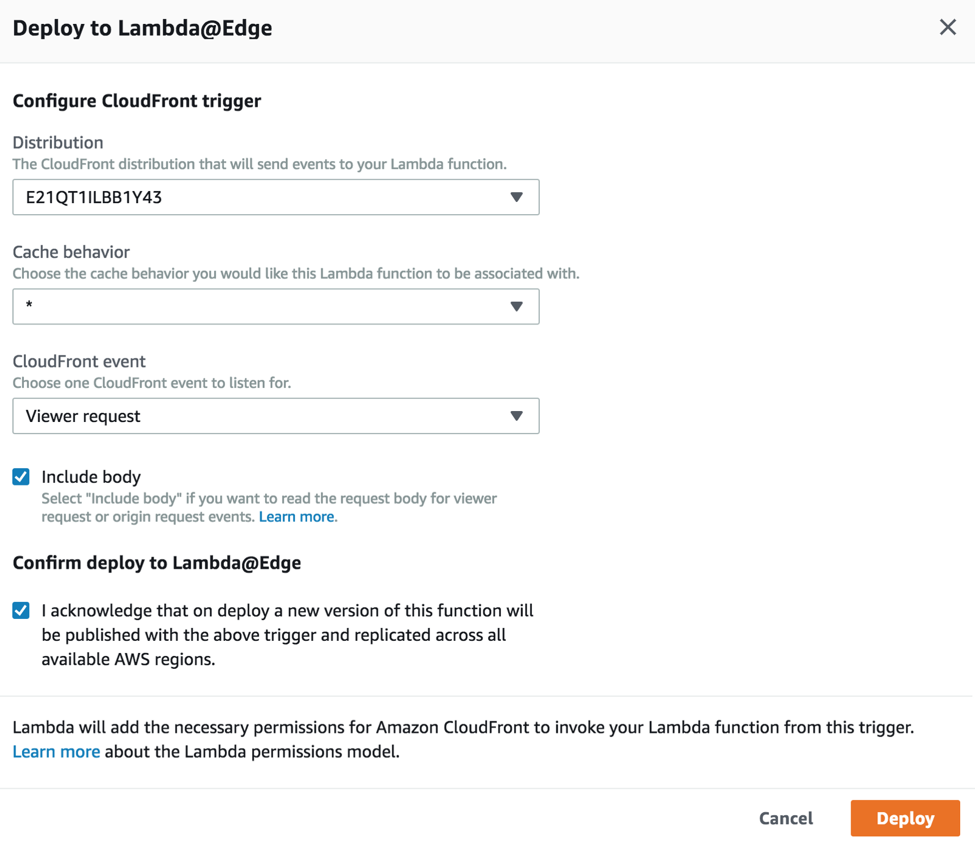
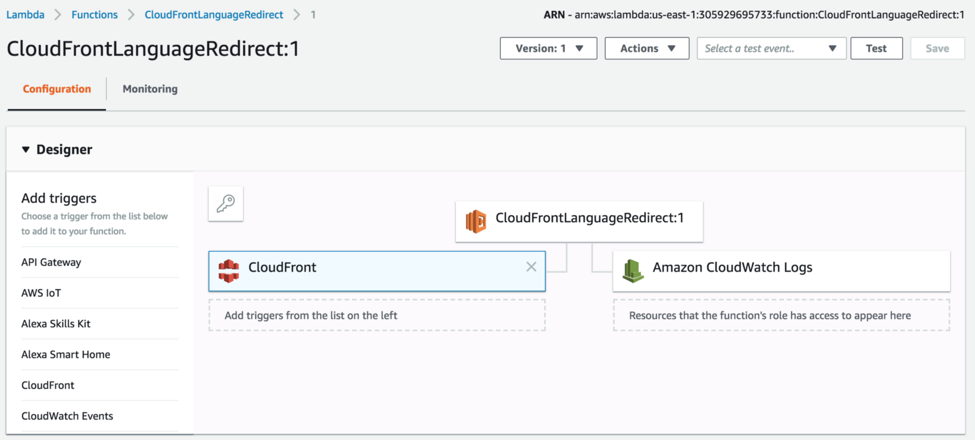
Click on “Deploy” and the Lambda function will start to run as soon as it finishes replicating to AWS edge locations around the world:
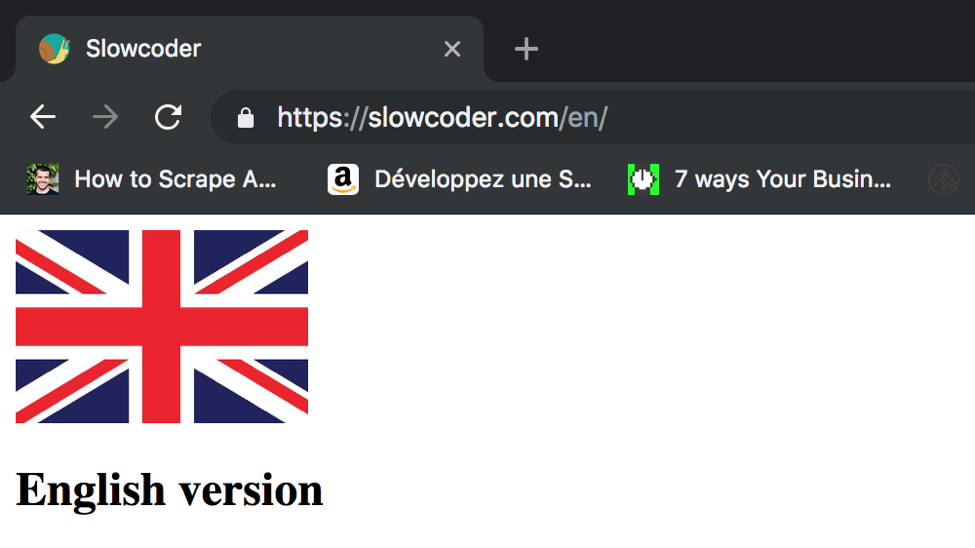
To test it out, point your favorite web browser to the website URL, you should be redirected automatically to the english version of the website:
If you change your browser default language. For Chrome browser follow the steps below:
- At the top right, click on “Settings”.
- At the bottom, click “Advanced”.
- Under “Languages,” click “Language”.
- Set the language you’d like to use
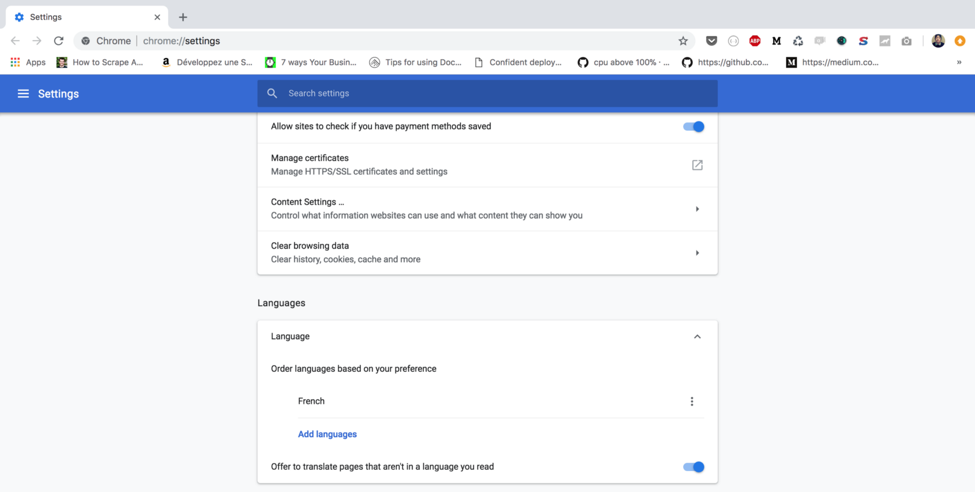
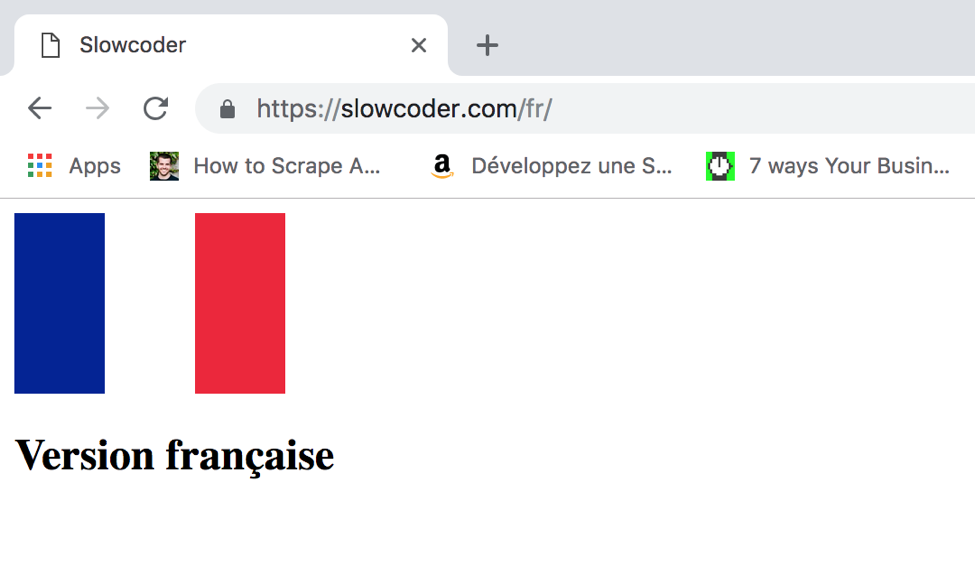
In the screenshot above, I set French to be my browser language. Once the browser is restarted (needed for updates to take effect), you will be redirected automatically to the French version of the website:
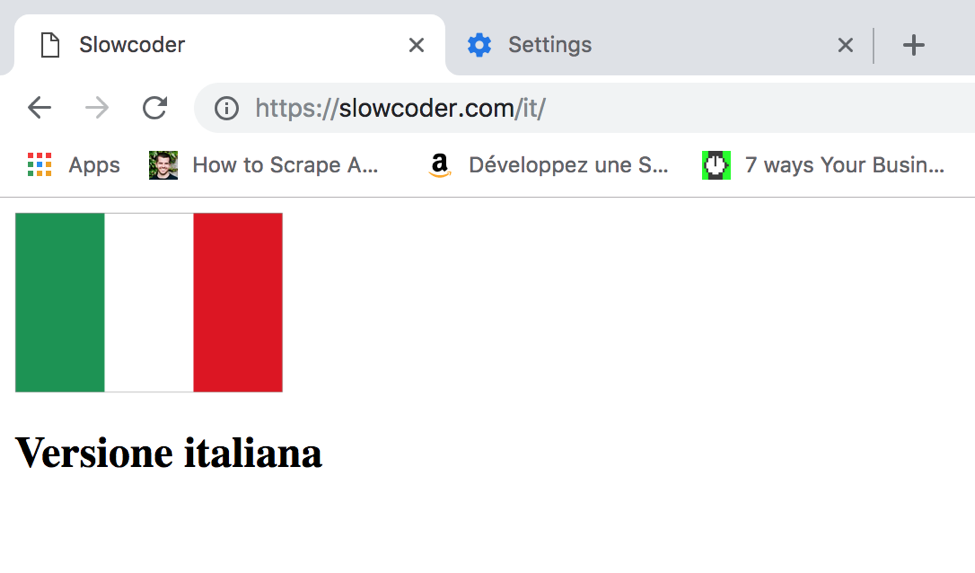
Once again, change your browser language to Italian as follows:
You will be redirected automatically to the Italian homepage:
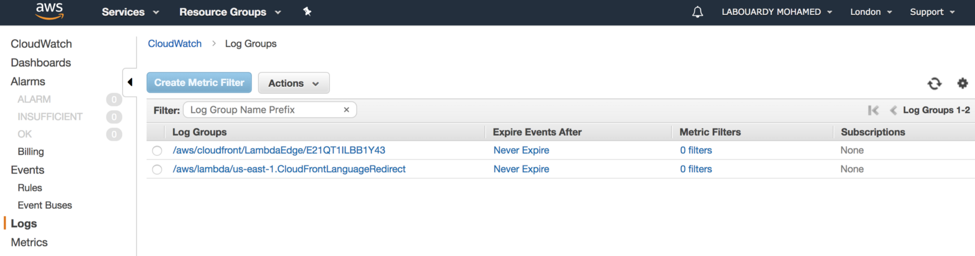
PS: for debugging, Lambda@Edge stream CloudWatch logs to the nearest AWS region closest to the location where the function executes in. In my case, the nearest region is London:
Like what you’re reading? Check out my book and learn how to build, secure, deploy and manage production-ready Serverless applications in Golang with AWS Lambda.
About the author:
Mohamed Labouardy is a Software Engineer/DevOps Engineer, 5x AWS Certified and Scrum Master Certified. He is interested in Serverless Architecture, Containers, Distributed Systems, Go & NLP. A Contributor to numerous Open Source projects such as DialogFlow, Jenkins, Docker, Nexus and Telegraf. He authored some Open Source projects related to DevOps as well. Check out his website here.